Path: blob/master/examples/vision/depth_estimation.py
3507 views
"""1Title: Monocular depth estimation2Author: [Victor Basu](https://www.linkedin.com/in/victor-basu-520958147)3Date created: 2021/08/304Last modified: 2024/08/135Description: Implement a depth estimation model with a convnet.6Accelerator: GPU7"""89"""10## Introduction1112_Depth estimation_ is a crucial step towards inferring scene geometry from 2D images.13The goal in _monocular depth estimation_ is to predict the depth value of each pixel or14inferring depth information, given only a single RGB image as input.15This example will show an approach to build a depth estimation model with a convnet16and simple loss functions.1718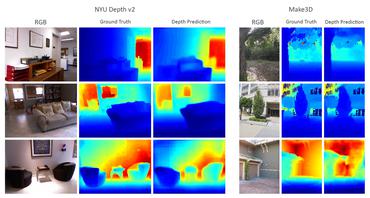1920"""2122"""23## Setup24"""2526import os2728os.environ["KERAS_BACKEND"] = "tensorflow"2930import sys3132import tensorflow as tf33import keras34from keras import layers35from keras import ops36import pandas as pd37import numpy as np38import cv239import matplotlib.pyplot as plt4041keras.utils.set_random_seed(123)4243"""44## Downloading the dataset4546We will be using the dataset **DIODE: A Dense Indoor and Outdoor Depth Dataset** for this47tutorial. However, we use the validation set generating training and evaluation subsets48for our model. The reason we use the validation set rather than the training set of the original dataset is because49the training set consists of 81GB of data, which is challenging to download compared50to the validation set which is only 2.6GB.51Other datasets that you could use are52**[NYU-v2](https://cs.nyu.edu/~silberman/datasets/nyu_depth_v2.html)**53and **[KITTI](http://www.cvlibs.net/datasets/kitti/)**.54"""5556annotation_folder = "/dataset/"57if not os.path.exists(os.path.abspath(".") + annotation_folder):58annotation_zip = keras.utils.get_file(59"val.tar.gz",60cache_subdir=os.path.abspath("."),61origin="http://diode-dataset.s3.amazonaws.com/val.tar.gz",62extract=True,63)6465"""66## Preparing the dataset6768We only use the indoor images to train our depth estimation model.69"""7071path = "val/indoors"7273filelist = []7475for root, dirs, files in os.walk(path):76for file in files:77filelist.append(os.path.join(root, file))7879filelist.sort()80data = {81"image": [x for x in filelist if x.endswith(".png")],82"depth": [x for x in filelist if x.endswith("_depth.npy")],83"mask": [x for x in filelist if x.endswith("_depth_mask.npy")],84}85df = pd.DataFrame(data)8687df = df.sample(frac=1, random_state=42)8889"""90## Preparing hyperparameters91"""9293HEIGHT = 25694WIDTH = 25695LR = 0.0000196EPOCHS = 3097BATCH_SIZE = 329899"""100## Building a data pipeline1011021. The pipeline takes a dataframe containing the path for the RGB images,103as well as the depth and depth mask files.1042. It reads and resize the RGB images.1053. It reads the depth and depth mask files, process them to generate the depth map image and106resize it.1074. It returns the RGB images and the depth map images for a batch.108"""109110111class DataGenerator(keras.utils.PyDataset):112def __init__(self, data, batch_size=6, dim=(768, 1024), n_channels=3, shuffle=True):113super().__init__()114"""115Initialization116"""117self.data = data118self.indices = self.data.index.tolist()119self.dim = dim120self.n_channels = n_channels121self.batch_size = batch_size122self.shuffle = shuffle123self.min_depth = 0.1124self.on_epoch_end()125126def __len__(self):127return int(np.ceil(len(self.data) / self.batch_size))128129def __getitem__(self, index):130if (index + 1) * self.batch_size > len(self.indices):131self.batch_size = len(self.indices) - index * self.batch_size132# Generate one batch of data133# Generate indices of the batch134index = self.indices[index * self.batch_size : (index + 1) * self.batch_size]135# Find list of IDs136batch = [self.indices[k] for k in index]137x, y = self.data_generation(batch)138139return x, y140141def on_epoch_end(self):142"""143Updates indexes after each epoch144"""145self.index = np.arange(len(self.indices))146if self.shuffle == True:147np.random.shuffle(self.index)148149def load(self, image_path, depth_map, mask):150"""Load input and target image."""151152image_ = cv2.imread(image_path)153image_ = cv2.cvtColor(image_, cv2.COLOR_BGR2RGB)154image_ = cv2.resize(image_, self.dim)155image_ = tf.image.convert_image_dtype(image_, tf.float32)156157depth_map = np.load(depth_map).squeeze()158159mask = np.load(mask)160mask = mask > 0161162max_depth = min(300, np.percentile(depth_map, 99))163depth_map = np.clip(depth_map, self.min_depth, max_depth)164depth_map = np.log(depth_map, where=mask)165166depth_map = np.ma.masked_where(~mask, depth_map)167168depth_map = np.clip(depth_map, 0.1, np.log(max_depth))169depth_map = cv2.resize(depth_map, self.dim)170depth_map = np.expand_dims(depth_map, axis=2)171depth_map = tf.image.convert_image_dtype(depth_map, tf.float32)172173return image_, depth_map174175def data_generation(self, batch):176x = np.empty((self.batch_size, *self.dim, self.n_channels))177y = np.empty((self.batch_size, *self.dim, 1))178179for i, batch_id in enumerate(batch):180x[i,], y[i,] = self.load(181self.data["image"][batch_id],182self.data["depth"][batch_id],183self.data["mask"][batch_id],184)185x, y = x.astype("float32"), y.astype("float32")186return x, y187188189"""190## Visualizing samples191"""192193194def visualize_depth_map(samples, test=False, model=None):195input, target = samples196cmap = plt.cm.jet197cmap.set_bad(color="black")198199if test:200pred = model.predict(input)201fig, ax = plt.subplots(6, 3, figsize=(50, 50))202for i in range(6):203ax[i, 0].imshow((input[i].squeeze()))204ax[i, 1].imshow((target[i].squeeze()), cmap=cmap)205ax[i, 2].imshow((pred[i].squeeze()), cmap=cmap)206207else:208fig, ax = plt.subplots(6, 2, figsize=(50, 50))209for i in range(6):210ax[i, 0].imshow((input[i].squeeze()))211ax[i, 1].imshow((target[i].squeeze()), cmap=cmap)212213214visualize_samples = next(215iter(DataGenerator(data=df, batch_size=6, dim=(HEIGHT, WIDTH)))216)217visualize_depth_map(visualize_samples)218219"""220## 3D point cloud visualization221"""222223depth_vis = np.flipud(visualize_samples[1][1].squeeze()) # target224img_vis = np.flipud(visualize_samples[0][1].squeeze()) # input225226fig = plt.figure(figsize=(15, 10))227ax = plt.axes(projection="3d")228229STEP = 3230for x in range(0, img_vis.shape[0], STEP):231for y in range(0, img_vis.shape[1], STEP):232ax.scatter(233[depth_vis[x, y]] * 3,234[y] * 3,235[x] * 3,236c=tuple(img_vis[x, y, :3] / 255),237s=3,238)239ax.view_init(45, 135)240241"""242## Building the model2432441. The basic model is from U-Net.2452. Addditive skip-connections are implemented in the downscaling block.246"""247248249class DownscaleBlock(layers.Layer):250def __init__(251self, filters, kernel_size=(3, 3), padding="same", strides=1, **kwargs252):253super().__init__(**kwargs)254self.convA = layers.Conv2D(filters, kernel_size, strides, padding)255self.convB = layers.Conv2D(filters, kernel_size, strides, padding)256self.reluA = layers.LeakyReLU(negative_slope=0.2)257self.reluB = layers.LeakyReLU(negative_slope=0.2)258self.bn2a = layers.BatchNormalization()259self.bn2b = layers.BatchNormalization()260261self.pool = layers.MaxPool2D((2, 2), (2, 2))262263def call(self, input_tensor):264d = self.convA(input_tensor)265x = self.bn2a(d)266x = self.reluA(x)267268x = self.convB(x)269x = self.bn2b(x)270x = self.reluB(x)271272x += d273p = self.pool(x)274return x, p275276277class UpscaleBlock(layers.Layer):278def __init__(279self, filters, kernel_size=(3, 3), padding="same", strides=1, **kwargs280):281super().__init__(**kwargs)282self.us = layers.UpSampling2D((2, 2))283self.convA = layers.Conv2D(filters, kernel_size, strides, padding)284self.convB = layers.Conv2D(filters, kernel_size, strides, padding)285self.reluA = layers.LeakyReLU(negative_slope=0.2)286self.reluB = layers.LeakyReLU(negative_slope=0.2)287self.bn2a = layers.BatchNormalization()288self.bn2b = layers.BatchNormalization()289self.conc = layers.Concatenate()290291def call(self, x, skip):292x = self.us(x)293concat = self.conc([x, skip])294x = self.convA(concat)295x = self.bn2a(x)296x = self.reluA(x)297298x = self.convB(x)299x = self.bn2b(x)300x = self.reluB(x)301302return x303304305class BottleNeckBlock(layers.Layer):306def __init__(307self, filters, kernel_size=(3, 3), padding="same", strides=1, **kwargs308):309super().__init__(**kwargs)310self.convA = layers.Conv2D(filters, kernel_size, strides, padding)311self.convB = layers.Conv2D(filters, kernel_size, strides, padding)312self.reluA = layers.LeakyReLU(negative_slope=0.2)313self.reluB = layers.LeakyReLU(negative_slope=0.2)314315def call(self, x):316x = self.convA(x)317x = self.reluA(x)318x = self.convB(x)319x = self.reluB(x)320return x321322323"""324## Defining the loss325326We will optimize 3 losses in our mode.3271. Structural similarity index(SSIM).3282. L1-loss, or Point-wise depth in our case.3293. Depth smoothness loss.330331Out of the three loss functions, SSIM contributes the most to improving model performance.332"""333334335def image_gradients(image):336if len(ops.shape(image)) != 4:337raise ValueError(338"image_gradients expects a 4D tensor "339"[batch_size, h, w, d], not {}.".format(ops.shape(image))340)341342image_shape = ops.shape(image)343batch_size, height, width, depth = ops.unstack(image_shape)344345dy = image[:, 1:, :, :] - image[:, :-1, :, :]346dx = image[:, :, 1:, :] - image[:, :, :-1, :]347348# Return tensors with same size as original image by concatenating349# zeros. Place the gradient [I(x+1,y) - I(x,y)] on the base pixel (x, y).350shape = ops.stack([batch_size, 1, width, depth])351dy = ops.concatenate([dy, ops.zeros(shape, dtype=image.dtype)], axis=1)352dy = ops.reshape(dy, image_shape)353354shape = ops.stack([batch_size, height, 1, depth])355dx = ops.concatenate([dx, ops.zeros(shape, dtype=image.dtype)], axis=2)356dx = ops.reshape(dx, image_shape)357358return dy, dx359360361class DepthEstimationModel(keras.Model):362def __init__(self):363super().__init__()364self.ssim_loss_weight = 0.85365self.l1_loss_weight = 0.1366self.edge_loss_weight = 0.9367self.loss_metric = keras.metrics.Mean(name="loss")368f = [16, 32, 64, 128, 256]369self.downscale_blocks = [370DownscaleBlock(f[0]),371DownscaleBlock(f[1]),372DownscaleBlock(f[2]),373DownscaleBlock(f[3]),374]375self.bottle_neck_block = BottleNeckBlock(f[4])376self.upscale_blocks = [377UpscaleBlock(f[3]),378UpscaleBlock(f[2]),379UpscaleBlock(f[1]),380UpscaleBlock(f[0]),381]382self.conv_layer = layers.Conv2D(1, (1, 1), padding="same", activation="tanh")383384def calculate_loss(self, target, pred):385# Edges386dy_true, dx_true = image_gradients(target)387dy_pred, dx_pred = image_gradients(pred)388weights_x = ops.cast(ops.exp(ops.mean(ops.abs(dx_true))), "float32")389weights_y = ops.cast(ops.exp(ops.mean(ops.abs(dy_true))), "float32")390391# Depth smoothness392smoothness_x = dx_pred * weights_x393smoothness_y = dy_pred * weights_y394395depth_smoothness_loss = ops.mean(abs(smoothness_x)) + ops.mean(396abs(smoothness_y)397)398399# Structural similarity (SSIM) index400ssim_loss = ops.mean(4011402- tf.image.ssim(403target, pred, max_val=WIDTH, filter_size=7, k1=0.01**2, k2=0.03**2404)405)406# Point-wise depth407l1_loss = ops.mean(ops.abs(target - pred))408409loss = (410(self.ssim_loss_weight * ssim_loss)411+ (self.l1_loss_weight * l1_loss)412+ (self.edge_loss_weight * depth_smoothness_loss)413)414415return loss416417@property418def metrics(self):419return [self.loss_metric]420421def train_step(self, batch_data):422input, target = batch_data423with tf.GradientTape() as tape:424pred = self(input, training=True)425loss = self.calculate_loss(target, pred)426427gradients = tape.gradient(loss, self.trainable_variables)428self.optimizer.apply_gradients(zip(gradients, self.trainable_variables))429self.loss_metric.update_state(loss)430return {431"loss": self.loss_metric.result(),432}433434def test_step(self, batch_data):435input, target = batch_data436437pred = self(input, training=False)438loss = self.calculate_loss(target, pred)439440self.loss_metric.update_state(loss)441return {442"loss": self.loss_metric.result(),443}444445def call(self, x):446c1, p1 = self.downscale_blocks[0](x)447c2, p2 = self.downscale_blocks[1](p1)448c3, p3 = self.downscale_blocks[2](p2)449c4, p4 = self.downscale_blocks[3](p3)450451bn = self.bottle_neck_block(p4)452453u1 = self.upscale_blocks[0](bn, c4)454u2 = self.upscale_blocks[1](u1, c3)455u3 = self.upscale_blocks[2](u2, c2)456u4 = self.upscale_blocks[3](u3, c1)457458return self.conv_layer(u4)459460461"""462## Model training463"""464465optimizer = keras.optimizers.SGD(466learning_rate=LR,467nesterov=False,468)469model = DepthEstimationModel()470# Compile the model471model.compile(optimizer)472473train_loader = DataGenerator(474data=df[:260].reset_index(drop="true"), batch_size=BATCH_SIZE, dim=(HEIGHT, WIDTH)475)476validation_loader = DataGenerator(477data=df[260:].reset_index(drop="true"), batch_size=BATCH_SIZE, dim=(HEIGHT, WIDTH)478)479model.fit(480train_loader,481epochs=EPOCHS,482validation_data=validation_loader,483)484485"""486## Visualizing model output487488We visualize the model output over the validation set.489The first image is the RGB image, the second image is the ground truth depth map image490and the third one is the predicted depth map image.491"""492493test_loader = next(494iter(495DataGenerator(496data=df[265:].reset_index(drop="true"), batch_size=6, dim=(HEIGHT, WIDTH)497)498)499)500visualize_depth_map(test_loader, test=True, model=model)501502test_loader = next(503iter(504DataGenerator(505data=df[300:].reset_index(drop="true"), batch_size=6, dim=(HEIGHT, WIDTH)506)507)508)509visualize_depth_map(test_loader, test=True, model=model)510511"""512## Possible improvements5135141. You can improve this model by replacing the encoding part of the U-Net with a515pretrained DenseNet or ResNet.5162. Loss functions play an important role in solving this problem.517Tuning the loss functions may yield significant improvement.518"""519520"""521## References522523The following papers go deeper into possible approaches for depth estimation.5241. [Depth Prediction Without the Sensors: Leveraging Structure for Unsupervised Learning from Monocular Videos](https://arxiv.org/abs/1811.06152v1)5252. [Digging Into Self-Supervised Monocular Depth Estimation](https://openaccess.thecvf.com/content_ICCV_2019/papers/Godard_Digging_Into_Self-Supervised_Monocular_Depth_Estimation_ICCV_2019_paper.pdf)5263. [Deeper Depth Prediction with Fully Convolutional Residual Networks](https://arxiv.org/abs/1606.00373v2)527528You can also find helpful implementations in the papers with code depth estimation task.529530You can use the trained model hosted on [Hugging Face Hub](https://huggingface.co/spaces/keras-io/Monocular-Depth-Estimation)531and try the demo on [Hugging Face Spaces](https://huggingface.co/keras-io/monocular-depth-estimation).532"""533534535